
Indices Trading
On this page, you can find in-depth information about Indices Trading. Whether you're just getting started with trading indices or looking for new strategies, TradingSheets.com equips you with everything you need to succeed in the world of indices.
How To Start Trading In 15 Minutes
Introduction to Indices Trading
What is Indices Trading?
Indices trading involves speculating on the price movements of a stock market index rather than individual stocks. A stock market index is a collection of several stocks that represent a portion of the market, such as the S&P 500 or the FTSE 100. When you trade indices, you’re essentially betting on whether the entire index will go up or down. This can give you exposure to a wide range of companies without having to invest in individual stocks.
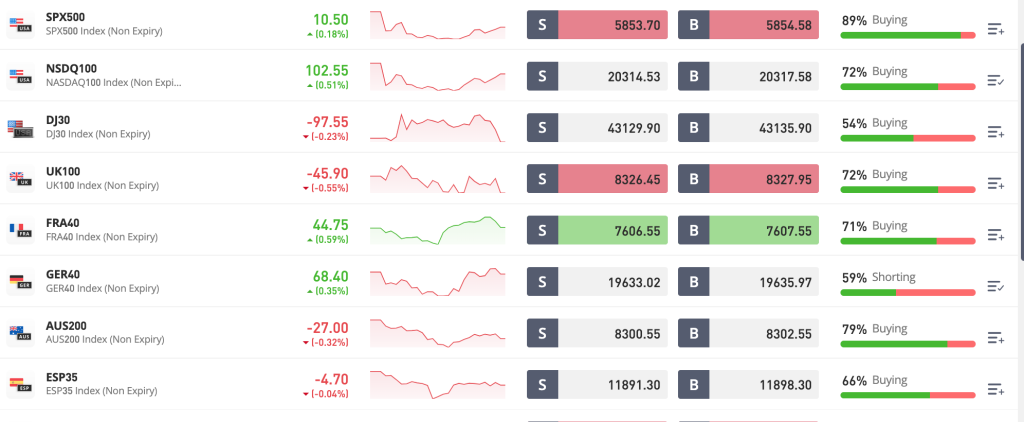
How Does Indices Trading Work?
Indices trading works by tracking the price movements of an index. If you think the value of the index will increase, you go long (buy). If you think it will decrease, you go short (sell). The value of the index depends on the performance of the companies within it. For example, if most of the companies in the S&P 500 perform well, the index will rise, and if they perform poorly, the index will fall.
You don’t actually buy or own the stocks in the index. Instead, you trade the index through financial products like contracts for difference (CFDs) or futures, which allow you to profit from price movements.
Key Benefits of Trading Indices
There are several advantages to trading indices, including:
- Diversification: Indices represent a broad range of companies, which means your risk is spread out rather than relying on the performance of one stock.
- Lower Volatility: Individual stocks can be highly volatile, while indices tend to be more stable since they represent the market as a whole.
- Cost-Effective: You can gain exposure to a wide range of companies without having to invest in each stock individually.
- 24/5 Trading: Many indices can be traded almost 24 hours a day, five days a week, giving you more flexibility in your trading schedule.
Indices Trading vs. Stock Trading: Key Differences
| Feature | Indices Trading | Stock Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | Groups of stocks (e.g., S&P 500, NASDAQ) | Individual company stocks |
| Risk | More diversified, lower risk | Higher risk as focused on one company |
| Volatility | Generally less volatile | Can be highly volatile depending on the stock |
| Costs | Fewer transactions, more cost-effective | Buying multiple stocks can be costly |
Popular Stock Market Indices to Trade
Some of the most popular stock market indices that traders follow include:
- S&P 500: Represents 500 of the largest companies in the U.S. and is a key indicator of U.S. market health.
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA): Tracks 30 large publicly-owned companies in the U.S. and is another widely followed index.
- NASDAQ 100: Comprises 100 of the largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ exchange, with a heavy focus on tech.
- FTSE 100: Represents the 100 largest companies on the London Stock Exchange.
- DAX 40: Tracks 40 major companies in Germany and is a strong indicator of European market performance.
Getting Started with Indices Trading
What You Need to Start Trading Indices
To start trading indices, you’ll need a few basic things:
- A Trading Account: This is the account you’ll use to access the market and place trades.
- A Broker: You’ll need a broker that offers access to index trading, preferably one that is regulated and trustworthy.
- A Trading Platform: This is the software you use to place trades and analyze the markets.
- Initial Capital: Even though you can start small, you will need some capital to open and maintain your positions.
- Knowledge and Strategy: It’s essential to understand how the market works and have a solid trading strategy.
Choosing a Broker for Indices Trading
When selecting a broker for indices trading, you should look for the following:
- Regulation: Choose a broker that is regulated by a reliable financial authority. This ensures that your funds are protected.
- Fees and Spreads: Look for brokers with low trading costs. Spreads (the difference between the buy and sell price) can eat into your profits.
- Trading Platform: The broker should offer a user-friendly trading platform with tools for analyzing the market.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential if you encounter any issues with your trades or account.
Types of Trading Accounts for Indices
There are different types of accounts you can use when trading indices:
- Standard Account: This is the most common type of trading account, allowing you to trade regular lot sizes.
- Mini Account: A mini account is for traders who want to trade smaller positions. You trade mini lots, which are one-tenth the size of a standard lot.
- Micro Account: Ideal for beginners, micro accounts allow you to trade micro lots, which are even smaller than mini lots. This is a low-risk way to get started.
Understanding Index Components and How They Are Calculated
Each index is made up of different companies, and the value of the index is calculated based on the performance of these companies. For example:
- Price-Weighted Indices: In a price-weighted index like the DJIA, companies with higher stock prices have more influence on the index’s movement.
- Market-Cap-Weighted Indices: In a market-cap-weighted index like the S&P 500, companies with a larger market capitalization (total value of their stocks) have more weight in determining the index’s value.
Trading Platforms for Indices Trading
Popular trading platforms for indices trading include:
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4): A widely-used platform with comprehensive charting tools.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5): The updated version of MT4 with more advanced features.
- cTrader: Known for its fast execution and advanced charting capabilities.
- TradingView: A powerful web-based platform with strong technical analysis tools.
Indices Trading Strategies for Beginners
Introduction to Basic Indices Trading Strategies
Indices trading strategies are methods traders use to determine when to enter and exit trades. For beginners, it’s crucial to start with simple strategies and gradually progress to more complex ones. Below are some basic strategies you can try.
Day Trading Indices: Quick Profits and High Risk
Day trading involves opening and closing trades within the same day. Traders look for short-term price movements and aim to profit from small fluctuations. This strategy requires quick decision-making and constant monitoring of the market. Day trading can be high risk but also offers the potential for quick profits. Popular indices for day trading include the NASDAQ 100 and S&P 500 due to their volatility.
Swing Trading Indices: Capturing Mid-Term Trends
Swing trading is a more relaxed strategy where traders hold positions for a few days to weeks. The idea is to capture trends that develop over several days and ride the price swings. Swing trading requires less time commitment compared to day trading and is suitable for traders looking for moderate risk and reward. It’s ideal for trading major indices like the FTSE 100 and DAX 40, which often exhibit clear trends.
Position Trading Indices: Long-Term Investment Approach
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold their positions for months or even years. This strategy is based on fundamental analysis and aims to capture major market trends over time. Position traders are less concerned with short-term price fluctuations and focus more on long-term market direction. It’s best suited for those looking for minimal time involvement while maintaining a long-term view of the market.
Scalping Strategy in Indices Trading
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders make dozens or even hundreds of trades in a single day, aiming to profit from small price movements. Each trade typically lasts only a few seconds or minutes. Scalping requires quick execution and often relies on tight spreads. While profits per trade are small, scalpers aim to accumulate many small gains throughout the day. Indices like the NASDAQ 100 are popular among scalpers due to their high volatility.
Scalping can be effective, but it also demands full attention and a strong understanding of the market, making it more suitable for experienced traders.
Advanced Indices Trading Techniques
Trend Following in Indices: Riding the Market Waves
Trend following is a strategy where traders aim to profit by riding long-term trends in the market. The basic idea is simple: when an index is trending upward, you buy, and when it’s trending downward, you sell. Traders use technical indicators like moving averages to confirm the direction of the trend and then enter positions accordingly. The goal is to capture profits from the sustained movement of the market, rather than short-term fluctuations.
Trend following works best during periods of strong market momentum and is most effective on indices that show clear, sustained trends, such as the S&P 500 or the FTSE 100.
Range Trading in Indices: Profiting from Sideways Movements
Range trading is a strategy used when the market is moving sideways, bouncing between defined support and resistance levels. Traders buy when the index is near the support level and sell when it approaches the resistance level. This strategy is useful in markets where prices fluctuate within a set range without forming a strong trend.
The key to successful range trading is identifying the boundaries of the range and knowing when the price is likely to reverse. Tools like Bollinger Bands or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can help traders identify these levels and time their trades more accurately.
Using Fibonacci Retracement in Indices Trading
Fibonacci retracement is a popular tool used to identify potential reversal levels in the market. Traders use the Fibonacci sequence to predict where an index might pull back before continuing in the direction of the trend. The key retracement levels to watch are 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%, which are seen as areas where price corrections might occur.
For example, in a strong uptrend, traders look for the price to pull back to one of these levels before resuming its upward movement. This tool is particularly useful in volatile indices like the NASDAQ 100.
Algorithmic Trading in Indices
Algorithmic trading, also known as automated trading, involves using pre-programmed algorithms to execute trades based on defined criteria, such as price, volume, or technical indicators. These algorithms can scan the market and execute trades faster than any human could, making them ideal for high-frequency trading strategies or managing multiple positions.
Algorithmic trading is commonly used by institutional traders, but retail traders can also access these tools through brokers that offer automated trading features. It’s particularly useful for traders looking to minimize emotional decisions and optimize their trading strategy based on data.
Technical Analysis Tools for Indices Traders
Technical analysis tools help traders analyze price movements and identify potential trading opportunities. Some of the best indicators for indices trading include:
- Moving Averages: Help smooth out price data to identify the direction of the trend.
- Bollinger Bands: Measure volatility and help identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Shows whether an index is overbought or oversold, helping traders time their entries and exits.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): A momentum indicator that helps traders identify trend changes and momentum shifts.
Using these tools together can help traders build a clearer picture of market conditions and make more informed decisions.
Indices Risk Management
The Importance of Risk Management in Indices Trading
Risk management is one of the most important aspects of indices trading. Without proper risk control, even the most successful strategy can lead to significant losses. The goal of risk management is to protect your capital while maximizing profit potential. This includes setting clear rules for how much you are willing to risk on each trade and making sure that losses are limited through stop-loss orders.
By controlling risk, you can survive losing streaks and keep your capital intact to take advantage of future trading opportunities.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels in Indices Trading
Stop-loss and take-profit levels are crucial tools for managing risk. A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when the price moves against you, limiting your losses. For example, if you buy an index and set a stop-loss 50 points below your entry price, the trade will close once the price drops by 50 points, preventing further loss.
A take-profit order does the opposite: it closes the trade when the price reaches a predetermined profit target. This helps lock in profits without the need to constantly monitor the market.
Both stop-loss and take-profit orders ensure that you maintain discipline and don’t let emotions influence your trading decisions.
How to Calculate Risk-Reward Ratios in Indices Trading
The risk-reward ratio is a key metric that helps you assess whether a trade is worth taking. It compares the potential profit of a trade to the amount of risk involved. For example, if you risk 50 points to gain 100 points, your risk-reward ratio is 1:2. In this case, the potential reward is twice the risk, making it a favorable trade setup.
As a rule of thumb, traders aim for a minimum risk-reward ratio of 1:2, meaning they expect to make twice as much as they risk on any given trade. This ensures that even with a few losing trades, your winning trades can keep you profitable.
Position Sizing in Indices Trading: How Much to Risk Per Trade
Position sizing refers to how much capital you allocate to a single trade. Proper position sizing helps ensure that no single trade can significantly damage your account. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total account balance on a single trade.
For example, if your account balance is $10,000 and you’re willing to risk 2%, you would risk $200 on a trade. This helps protect your capital and allows you to survive losing streaks without taking major hits to your account.
Hedging Strategies in Indices Trading
Hedging is a risk management strategy used to offset potential losses by taking a position in the opposite direction of your main trade. For example, if you are holding a long position in the S&P 500 but anticipate short-term market volatility, you might hedge by taking a short position in a related asset or using options contracts.
Hedging can help minimize losses when market conditions are uncertain, but it also limits your profit potential. It’s an advanced strategy often used by traders who want to protect their positions in volatile markets while maintaining long-term exposure to an index.
Fundamental Analysis for Indices Trading
Understanding Economic Indicators and Their Impact on Indices
Economic indicators are key metrics that give traders insight into the overall health of an economy and can heavily influence the movement of indices. Some of the most important indicators to track include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A growing GDP generally boosts investor confidence, leading to an increase in index values.
- Unemployment Rate: Higher unemployment signals economic weakness, which can negatively affect indices, while low unemployment typically boosts them.
- Inflation Data: Inflation impacts the purchasing power of consumers and influences central bank policy, affecting market sentiment and indices.
- Consumer Confidence: When consumers are confident about the economy, spending increases, which supports stock prices and indices.
- Retail Sales: Strong retail sales numbers indicate a healthy economy, which can push indices higher.
By staying on top of these reports, traders can anticipate market shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
How Central Bank Policies Affect Indices Trading
Central banks play a critical role in influencing the financial markets, including stock market indices. Decisions made by central banks, such as changes in interest rates or quantitative easing programs, can have direct impacts on market sentiment and the value of indices. For example:
- Interest Rate Hikes: When a central bank raises interest rates, borrowing costs increase, which can slow economic growth and negatively impact indices.
- Interest Rate Cuts: Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, which can push stock prices higher and boost indices.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): Central banks inject liquidity into the market through bond-buying programs, which typically raises stock prices and, in turn, indices.
Monitoring central bank decisions and statements is crucial for understanding the long-term outlook of indices and adapting your trading strategy accordingly.
Using Corporate Earnings Reports in Indices Trading
Corporate earnings reports are a key driver of individual stock prices, and when enough large companies report strong or weak earnings, it can have a significant impact on the indices they belong to. Traders should pay close attention to the earnings season, especially for companies that are heavily weighted in major indices.
- Positive Earnings Reports: When companies in an index beat earnings expectations, the index as a whole can rise.
- Negative Earnings Reports: Conversely, when major companies report poor earnings, it can drag the index down.
For example, tech-heavy indices like the NASDAQ 100 are particularly sensitive to the earnings reports of major technology companies.
Trading Indices Based on Economic News
Economic news, such as employment reports, inflation data, or GDP releases, often causes immediate reactions in indices. This strategy, known as news trading, involves capitalizing on these reactions by entering trades immediately before or after key news events.
- Pre-News Strategy: Traders may take positions based on their expectations of the news outcome, placing bets on whether the data will come in above or below expectations.
- Post-News Strategy: Some traders wait for the news release and then trade based on the market’s initial reaction. This can be a safer approach since it removes the uncertainty of predicting the news.
Trading on news requires close monitoring of an economic calendar and the ability to execute trades quickly, as price movements can be swift and volatile.
Global Events and Their Effect on Indices Markets
Global events such as political developments, natural disasters, trade disputes, or pandemics can have dramatic effects on indices. For example:
- Political Instability: Elections, protests, or government changes can lead to market uncertainty, which may cause indices to fall.
- Trade Wars: Tariffs and trade disputes between major economies can affect global supply chains, often leading to volatility in indices.
- Pandemics or Natural Disasters: These events can disrupt industries and economies, causing broad market sell-offs that affect major indices.
Staying informed about global events is crucial for managing risk in indices trading, as they can lead to sudden and unexpected market movements.
7. Indices Market Analysis
Top Tools for Analyzing Indices Markets
Traders rely on various tools to analyze indices markets and identify trading opportunities. Some of the most popular indices trading tools include:
- Economic Calendars: Provide a schedule of upcoming economic releases that could impact market movements.
- Charting Platforms: Tools like MetaTrader, TradingView, and cTrader offer advanced charting features to help traders perform technical analysis.
- Sentiment Indicators: Tools that show the percentage of traders who are long or short on a particular index, providing insight into market sentiment.
- Volume Indicators: Help traders understand how many shares or contracts are being traded, which can confirm the strength of a market move.
These tools allow traders to gain deeper insights into the behavior of indices and make more informed trading decisions.
How to Read Indices Charts
Indices charts provide a visual representation of price movements over time and are essential for technical analysis. The three most common types of charts are:
- Line Charts: Display the closing prices over a set period of time, providing a simple view of the overall market trend.
- Bar Charts: Show the opening, high, low, and closing prices for each time period, offering more detailed information than line charts.
- Candlestick Charts: Similar to bar charts but visually more intuitive, with “candles” representing price movements. Candlestick charts are popular among traders due to their ability to show clear patterns and reversals.
Learning how to read and interpret these charts is a fundamental skill for any indices trader.
Common Chart Patterns in Indices Trading
Chart patterns are key tools in technical analysis and help traders identify potential trend reversals or continuations. Some of the most commonly used patterns in indices trading include:
- Head and Shoulders: A reversal pattern that signals a change in the direction of the market trend.
- Double Top/Double Bottom: Indicate that the market has reached a strong resistance (double top) or support (double bottom) level and is likely to reverse.
- Triangles: Continuation patterns that suggest the market will break out in the direction of the existing trend after a period of consolidation.
These patterns can help traders anticipate market movements and plan their entries and exits more effectively.
Candlestick Patterns for Indices: A Beginner’s Guide
Candlestick patterns are a favorite among technical traders because they provide clear signals about market direction. Some of the most basic but effective candlestick patterns for indices trading include:
- Doji: A candle where the open and close prices are very close together, indicating market indecision and a potential reversal.
- Hammer: A bullish reversal pattern that forms after a downtrend, signaling that the market may start to move upward.
- Engulfing Pattern: A bullish or bearish pattern where the second candle completely engulfs the first, indicating a strong reversal in market sentiment.
Understanding and recognizing these patterns can help you anticipate potential market turns and adjust your trading strategy accordingly.
Technical vs. Fundamental Analysis: Which is Better for Indices Trading?
Both technical and fundamental analysis have their strengths, and the choice between the two often depends on your trading style.
- Technical Analysis: Ideal for short-term traders who rely on chart patterns, indicators, and price action to make decisions. It helps traders find precise entry and exit points and can be useful for day trading or swing trading indices.
- Fundamental Analysis: More suited for long-term traders who focus on economic data, corporate earnings, and global events to predict market trends. Position traders often use this approach to capture major market movements over time.
Many successful traders combine both approaches, using technical analysis for timing and fundamental analysis for understanding the broader market context.
Trading Indices with Leverage
What is Leverage in Indices Trading?
Leverage in indices trading allows traders to control larger positions in the market with a relatively small amount of capital. Essentially, it means borrowing funds from your broker to increase your buying power. For example, with a leverage of 10:1, you can control $10,000 worth of an index with just $1,000 of your own money.
Leverage can be highly beneficial for increasing potential profits, but it also amplifies potential losses. It is important to fully understand how leverage works and the risks involved before using it in your trading.
Risks and Benefits of High Leverage in Indices Trading
Benefits:
- Increased Profit Potential: Leverage allows traders to make larger profits with a smaller initial investment. A 1% price movement in the index can lead to significant returns if leverage is used.
- Capital Efficiency: Traders can take larger positions in the market without needing a large amount of capital upfront, allowing them to diversify their trades and manage their resources more effectively.
Risks:
- Magnified Losses: Just as leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses. A small price movement against your position can lead to substantial losses, potentially wiping out your entire investment.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against you, your broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to maintain your position. Failure to meet the margin requirement could result in the broker closing your position, resulting in losses.
How to Use Leverage Safely in Indices Trading
Using leverage safely requires discipline and strict risk management. Here are some key tips for managing leverage effectively:
- Start Small: Use lower leverage ratios, especially if you are a beginner. Many brokers allow you to adjust your leverage settings to more conservative levels, such as 5:1 or 10:1.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. This ensures that your trade will automatically close if the market moves against you by a certain amount.
- Risk Management: Do not risk more than 1-2% of your trading account on any single trade. This way, even if the trade goes against you, your losses are limited.
- Monitor the Market: Stay aware of market conditions, particularly during periods of high volatility. High leverage can be especially dangerous during unpredictable market movements.
Leverage Examples in Indices Trading
Here’s how different levels of leverage work in practice:
| Leverage Ratio | Trader’s Capital | Total Position Size | Potential Gain/Loss on 1% Market Movement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | $1,000 | $1,000 | ±$10 |
| 10:1 | $1,000 | $10,000 | ±$100 |
| 50:1 | $1,000 | $50,000 | ±$500 |
| 100:1 | $1,000 | $100,000 | ±$1,000 |
As shown, higher leverage magnifies both gains and losses, making it a double-edged sword.
Indices Trading for Different Account Sizes
Trading Indices with a Small Account: Is It Possible?
Yes, it is entirely possible to trade indices with a small account. Many brokers offer micro and mini accounts that allow you to trade with smaller capital, such as $100 or less. However, trading with a small account requires careful risk management, as the margin for error is smaller. The key is to focus on capital preservation while gradually building your account.
Micro Accounts for Indices Trading: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Low Entry Barrier: Micro accounts allow traders to start with as little as $100, making it accessible for beginners or those with limited capital.
- Lower Risk: By trading smaller positions, the risk of significant losses is reduced, making it easier to manage your trades.
- Experience Building: Micro accounts are an excellent way to gain real-world trading experience without risking a large amount of money.
Cons:
- Limited Profit Potential: Because the position sizes are smaller, the profit potential is also limited, which may make it harder to grow your account quickly.
- Higher Relative Fees: Some brokers charge higher fees for micro accounts, which can eat into profits, especially if you’re making frequent trades.
Trading Indices with $100: Tips for Beginners
Trading indices with a $100 account is possible, but it requires extra caution and planning. Here are some tips:
- Use Low Leverage: Stick to low leverage ratios like 5:1 or 10:1 to minimize the risk of losing your capital quickly.
- Focus on Major Indices: Trade highly liquid indices like the S&P 500 or NASDAQ 100, which tend to have tighter spreads and more predictable price movements.
- Trade Micro Lots: Use a broker that offers micro lot trading, so you can take smaller positions and reduce your exposure.
- Practice with a Demo Account: Before trading with real money, practice on a demo account to get a feel for how the market moves and how leverage affects your trades.
Scaling Up Your Indices Trading Account: How to Grow Capital
Once you’ve gained confidence and experience, the goal becomes scaling up your account. Here are some strategies to grow your capital over time:
- Reinvest Profits: Rather than withdrawing profits immediately, reinvest them to take larger positions and increase your potential returns.
- Use a Consistent Strategy: Stick to a proven trading strategy that has worked for you in the past. Consistency is key to long-term success.
- Gradually Increase Position Sizes: As your account grows, you can slowly increase your position sizes while still adhering to your risk management rules. Avoid increasing your risk per trade drastically.
- Diversify Your Trades: As your account grows, consider diversifying by trading multiple indices. This spreads your risk and increases your chances of success in different market conditions.
By following these strategies, you can grow your trading account steadily without exposing yourself to unnecessary risk.
Psychology of Indices Trading
Managing Emotions in Indices Trading
Emotions can have a significant impact on trading performance, and managing them effectively is crucial for success. Fear and greed are two of the most common emotions traders experience. Fear can prevent you from taking a well-calculated risk, while greed can lead to overtrading or holding onto a losing position for too long. The key to managing emotions is to have a clear trading plan in place and to stick to it, regardless of market conditions. By doing so, you reduce the likelihood of making emotional decisions that could negatively affect your results.
Developing a Trading Plan and Sticking to It
A well-defined trading plan is essential for maintaining discipline in indices trading. Your plan should outline your entry and exit points, risk management rules, and the amount of capital you are willing to risk on each trade. Sticking to your plan is equally important. It prevents you from making impulsive decisions, which are often driven by emotions rather than logic. A solid trading plan not only helps protect your capital but also promotes consistent, disciplined trading practices.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Indices Trading
There are several common mistakes that traders should avoid. Overtrading is one of the most frequent errors, where traders open too many positions in hopes of making quick profits. Another common mistake is failing to set stop-loss orders, which can result in significant losses if the market moves against you. Not managing risk properly or using too much leverage can also lead to devastating losses. By avoiding these mistakes and focusing on a sound strategy, traders can improve their chances of long-term success.
Patience and Discipline: Key Traits for Indices Traders
Patience and discipline are two of the most important traits that successful traders possess. Indices trading is not about making quick profits but about being consistent over time. Patience allows traders to wait for the right market conditions to enter a trade, rather than rushing into a position. Discipline ensures that traders follow their plan, even when the market is volatile or unpredictable. These traits are crucial for navigating the ups and downs of the market and maintaining long-term profitability.
Building the Right Mindset for Success
To succeed in indices trading, it is important to build a resilient mindset. This means accepting that losses are part of the trading process and not letting them affect your confidence. A successful trader is one who views losses as learning opportunities and remains focused on the bigger picture. It’s also important to remain adaptable, as market conditions can change rapidly. A flexible mindset allows traders to adjust their strategies when necessary without becoming emotionally attached to specific trades.
Conclusion: Is Indices Trading Right for You?
Pros and Cons of Indices Trading
Pros
- Diversification: Trading indices gives you exposure to a basket of stocks, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual companies.
- Liquidity: Major indices like the S&P 500 and NASDAQ 100 are highly liquid, meaning trades can be executed quickly and at competitive prices.
- Leverage: Indices trading often offers access to leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with smaller amounts of capital.
- 24/5 Trading: Many indices can be traded nearly around the clock, providing flexibility in trading hours.
Cons
- Volatility: While volatility can provide trading opportunities, it also increases the risk of sudden market moves.
- Complexity: Indices trading requires an understanding of economic indicators, global events, and market sentiment, which can be challenging for beginners.
- Leverage Risks: While leverage can magnify profits, it also magnifies losses, making it essential to use leverage carefully.
What to Expect as an Indices Trader
As an indices trader, you can expect a fast-paced environment where both short-term and long-term strategies can be employed. Indices are influenced by a variety of factors, including economic data, corporate earnings, and geopolitical events. Traders need to be prepared to monitor market news and adjust their positions accordingly. Risk management is crucial in indices trading, as market conditions can change rapidly, leading to large price swings.
Is Indices Trading Profitable?
Indices trading can be profitable, but it requires a disciplined approach and a sound understanding of the market. Traders who succeed in indices trading typically have a well-defined strategy, strict risk management rules, and the patience to wait for the right opportunities. While there is potential for significant profits, indices trading also comes with risk, and it is important to be realistic about the time and effort required to achieve consistent profitability.
Final Tips for Getting Started with Indices Trading
- Start with a demo account to practice trading without risking real money.
- Focus on major indices like the S&P 500 or NASDAQ 100, which offer liquidity and tight spreads.
- Develop a solid trading plan and stick to it, even during periods of market volatility.
- Use stop-loss orders to manage risk and protect your capital.
- Learn to read both fundamental and technical indicators to gain a well-rounded view of the market.
- Keep your emotions in check and avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements.
Start Your Trading Journey with TRADE.com
Open a Real Money Account
Sign up with TRADE.com and start trading Indices Trading with as little as $100.
Open a Real AccountOR
Practice with a Demo Account
Not ready to trade with real money? Start practicing with TRADE.com’s demo account.
Open a Demo Account









